객체 복사하기
객체를 복사하는 데 주로 쓰이는 방법은 아래와 같습니다.
| 방법 | 장점 | 단점 |
|---|---|---|
| JSON.stringify() & JSON.parse() | 간단하고 빠르게 깊은 복사를 할 수 있습니다. | Infinity, Functions, Date, RegExp 등의 유형은 유실됩니다. |
| Spread syntax | 가장 간단하게 객체를 얕게 복사합니다. | 중첩된 객체는 깊게 복사하지 못합니다. |
| Object.assign() | 간단하게 객체를 얕게 복사합니다. | 중첩된 객체는 깊게 복사하지 못합니다. |
| Recursive Deep Copy | Infinity, Functions, Date, RegExp도 깊게 복사합니다. | 순환 참조가 있는 객체를 받을 경우 무한 루프에 빠지게 됩니다. 직접 작성한 함수이므로 객체(ArrayBuffer, DataView…)복사 로직 직접 구현 및 다양한 테스트 필요합니다. |
| Recursive Deep Clone with WeakMap Caching | 순환 참조가 있는 객체도 지원하며 Infinity, Functions, Date, RegExp도 깊게 복사합니다. | 직접 작성한 함수이므로 객체(ArrayBuffer, DataView…)복사 로직 직접 구현 및 다양한 테스트 필요합니다. |
| Lodash - cloneDeep() | 모든 데이터 형식에 대해 깊게 복사합니다. | 외부 종속성이 추가됩니다. |
각 함수를 테스트하기에 앞서 person 이라는 객체를 생성해두겠습니다. 앞으로 이 객체를 이용하여 모든 함수 테스트를 진행할 것입니다.
Set Person Object
const person = {
name: "ben",
age: 20,
address: {
city: "seoul",
country: "korea",
},
getAge: function () {
return this.age;
},
birth: new Date(),
life: Infinity,
regT: /^[a-z0-9](\.|\+|\-?[a-z0-9]){1,39}@test\.com$/gm,
};JSON.stringify() & JSON.parse()
JSON.stringify 함수가 객체를 JSON 문자열로 변환합니다. (원본 객체에 대한 참조가 없어집니다) 그리고 JSON.parse 를 이용해 객체를 반환합니다.
이렇게 이 두 가지 함수를 이용하여 간단하게 객체의 깊은 복사본을 만들 수 있습니다. 이제 복사된 객체가 변경되어도 원본 객체는 그대로 유지됩니다.
const deepCopyObj = <T extends Record<string, any>>(obj: T): T => {
return JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj));
};
const deepCopyPerson = deepCopyObj(person);
console.log(person === deepCopyPerson);
// => false
deepCopyPerson.name = "tony";
console.log(person.name);
// => 'ben'
console.log(deepCopyPerson.name);
// => 'tony'
deepCopyPerson.address.city = "busan";
console.log(person.address.city);
// => 'seoul'
console.log(deepCopyPerson.address.city);
// => 'busan'이 방법을 사용할 때 꼭 알아둬야 할 사항들이 있습니다. ArrayBuffer, Map, Set, RegExp, Date functions, RegExp, Date 객체, Infinity 까지 복사하진 않습니다. 왜 그럴까요?
Date객체는 JSON으로 변환하는 과정에서 ISO 8601형식에 따라 문자열로 저장됩니다. 따 라서 원본 객체의Date객체는 복사 후 손실됩니다.reviver기능을 사용하면Date객체를 가져올 수 있긴 합니다.- 함수는 데이터가 아니라 더 복잡한 의미를 가진 동작이며 JSON에서 지원되는 엔티티가 아니기 때문에 복사 후 함수는 유지되지 않습니다.
- JSON에서 객체를 직렬화하고 역직렬화하는 방법의 특성으로 인해 느릴 것 같지만 대부분의 사람들이 이 방식을 채택하여 사용하여 V8이 적극적으로 최적화했기에 빠르게 복사본 을 얻을 수 있습니다.
즉, 복사된 객체에서 아래와 같이 데이터를 사용하려 한다면 예와 에러가 발생합니다.
deepCopyPerson.getAge();
// => TypeError: deepCopyPerson.getAge is not a function
deepCopyPerson.birth.getDate();
// => TypeError: deepCopyPerson.birth.getDate is not a function
deepCopyPerson.life;
// => null따라서 이 방법은 객체 내에 위와 같은 데이터가 없을 경우에 사용하면 됩니다.
Spread syntax
const copyObj = <T extends Record<string, any>>(obj: T): T => {
return { ...obj };
};
const copyPerson = copyObj(person);
console.log(person === copyPerson);
// => falseObject.assign()
const copyObj = <T extends Record<string, any>>(obj: T): T => {
return Object.assign({}, obj);
};
const copyPerson = copyObj(person);
console.log(person === copyPerson);
// => falseSpead 연산자나 Object.assign 은 최상위 속성을 복사합니다. 하지만 객체로서의 속성은 얕은 복사 후 에 참조로 복사되므로 원본 객체와 복사된 객체 간에 공유됩니다. MDN: Object.assign()을 이용한 예시를 코드로 들어보겠습니다.
// 중첩된 객체를 포함하는 복잡한 person 객체 전달
// 중첩된 객체 내의 속성을 변경할 때마다 원본 객체인 person의 동일한 속성도 변합니다
const copiedPerson = Object.assign({}, person);
copiedPerson.name = "tony";
copiedPerson.address.city = "busan";
console.log(person.name, copiedPerson.name);
// => 'tony', 'ben'
console.log(person.address.city, copiedPerson.address.city);
// => 'busan', 'busan'원래 객체의 name 속성은 그대로 유지 되었지만, city 속성은 재할당 작업으로 인해 변경되었습니다. (Spread syntax 도 마찬가지) 그래도 JSON 방식에 비해 다른 점은 functions, rRegExp, Date 객체, Infinity 까지 복사된다는 점입니다.
따라서 중첩된 객체 속성이 필요하지 않은 경우에는 좋은 복사 방법입니다.
Recursive Deep Clone Object
앞에서 다뤘던 문제(JS 내장 함수 및 함수가 손실되는 것)를 해결하며 깊은 복사를 실현하는 함수를 만들어 보겠습니다. 복사를 진행하다가 객체를 만나면 함수를 재귀적으로 실행해 깊은 복사를 실현하면 됩니다.
regExp 와 Date 객체를 복사하는 건 Lodash의 코드를 참고하여 작성했습니다.
const isObject = (value: any): boolean => {
return (typeof value === "object" || typeof value === "function") && value != null;
};
const cloneRegExp = (regExp: any): RegExp => {
const reFlags = /\w*$/;
const result = new regExp.constructor(regExp.source, reFlags.exec(regExp));
result.lastIndex = regExp.lastIndex;
return result;
};
const getTag = <T = any,>(value: T): string => {
if (value == null) {
return value === undefined ? "[object Undefined]" : "[object Null]";
}
return Object.prototype.toString.call(value);
};
/**
* `Set`, `Map`, `Boolean`, `Date`, `Number`, `String`, `RegExp` 태그가 있는 값만 복사를 진행합니다.
*/
const initCloneByTag = (obj: any, tag: string) => {
const Ctor = obj.constructor;
switch (tag) {
case "[object Boolean]":
case "[object Date]":
return new Ctor(+obj);
case "[object Number]":
case "[object String]":
return new Ctor(obj);
case "[object Set]":
case "[object Map]":
return new Ctor();
case "[object RegExp]":
return cloneRegExp(obj);
}
};
const isPrototype = (value: object): boolean => {
const Ctor = value && value.constructor;
const proto = (typeof Ctor === "function" && Ctor.prototype) || Object.prototype;
return value === proto;
};
const initCloneObject = (obj: any) => {
return typeof obj.constructor === "function" && !isPrototype(obj)
? Object.create(Object.getPrototypeOf(obj)) // 객체 생성
: {};
};
const initCloneArray = (array: any): any => {
const { length } = array;
const result = new array.constructor(length);
if (
length &&
typeof array[0] === "string" &&
Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(array, "index")
) {
result.index = array.index;
result.input = array.input;
}
return result;
};
const deepCopyObject = <T,>(obj: T): T => {
// 오브렉트 유형이 아닌 원시값이라면 그대로 반환합니다.
if (!isObject(obj)) {
return obj;
}
let result: any;
const isFunc = typeof obj === "function" && obj instanceof Function;
const tag = getTag(obj);
if (tag === "[object Object]" || (isFunc && !obj)) {
result = isFunc ? {} : initCloneObject(obj);
} else if (tag === "[object Array]") {
result = initCloneArray(obj);
} else if (isFunc) {
result = obj instanceof Function ? obj : () => {};
} else {
result = initCloneByTag(obj, tag);
}
for (const key in obj) {
if (Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(obj, key)) {
result[key] = deepCopyObject(obj[key]);
} else {
result[key] = value[key];
}
}
return result;
};
const copiedPerson = deepCopyObject(person);
console.log(person === copiedPerson);
// => false
copiedPerson.name = "tony";
copiedPerson.address.city = "busan";
copiedPerson.address.zipCode = "12345";
console.log(person.name);
// => 'ben'
console.log(copiedPerson.name);
// => 'tony'
console.log(person.address.city);
// => 'seoul'
console.log(copiedPerson.address.city);
// => 'busan'
console.log(person.address.zipCode);
// => undefined
console.log(copiedPerson.address.zipCode);
// => '12345'
console.log(copiedPerson.regT);
// => lastIndex: 0
dotAll: false;
flags: "gm";
global: true;
hasIndices: false;
ignoreCase: false;
multiline: true;
source: "^[a-z0-9](\\.|\\+|\\-?[a-z0-9]){1,39}@test\\.com$";
sticky: false;
unicode: false;중요한 것을 살펴보자면 typeof 가 아닌 toString 메소드를 사용했습니다.
이 둘의 가장 큰 차이점은 toString 은 메소드이기 때문에 오버라이딩이 가능한 반면, typeof 는 연산 자로 분류되기에 오버라이드가 불가능합니다. 즉, typeof 를 사용해서는 반환되는 결과를 조작하는 게 불가능하기에 toString 을 타입 체크로 사용하여 추가적인 문자열 파싱을 진행했습니다.
그래서 toStringTag 를 활용하여 Map, Set, Boolean, Date, Number, String, RegExp 태 그가 있는 값만 복사를 진행합니다.
만약 깊게 복사해야 할 객체가 지금 제작한 함수로 커버할 수 있는 범위라면 이대로 쓰는 게 가장 좋습니다 .
그리고 이 코드에는 몇 가지 문제가 있습니다.
첫 번재는 바이너리 데이터 관련 객체(TypedArray, ArrayBuffer, DataView…) 객체는 깊게 복사하지 않습니다. 저는 굳이 ArrayBuffer 객체까지 깊게 복사할 필요가 없어 추가해주진 않았습니다만, 이 부분에 대한 태그 케이스를 추가하여 ArrayBuffer를 복사하는 로직을 작성해주면 바이너리 관련 객체도 깊게 복사 할 수 있겠습니다.
두 번째는 순환 참조가 있는 객체를 복사해야 할 경우에는 무한하게 서로가 서로를 호출해서 호출 스택 (call stack)이 터져버리는 에러를 마주하게 됩니다. 이 문제를 해결하기 위해선 무한 루프에 빠지지 않도록 이전의 참조 맵을 유지하면서 전달 받은 객체를 통해 반복하여 복사하도록 해주면 됩니다. 객체가 맵에 저장되어 있다면 복사본이 반복되지 않고 그대로 반환되도록 하는 것입니다.
const deepCopyObject = <T,>(value: T, hash = new WeakMap<object, any>()): T => {
let result: any;
if (result !== undefined) {
return result;
}
// 오브렉트 유형이 아닌 원시값이라면 그대로 반환합니다.
if (!isObject(value)) {
return value;
}
// 순환 참조
if (hash.has(value as object)) return hash.get(value as object);
const isFunc = typeof value === "function";
const tag = getTag(value);
if (tag === "[object Object]" || (isFunc && !value)) {
result = isFunc ? {} : initCloneObject(value);
} else if (tag === "[object Array]") {
result = initCloneArray(value);
} else if (isFunc) {
result = value;
} else {
result = initCloneByTag(value, tag);
}
// hash에 복사할 객체를 저장합니다.
hash.set(value as object, result);
if (tag === "[object Map]") {
// @ts-ignore
value.forEach((subValue, key) => {
result.set(key, deepCopyObject(subValue, hash));
});
}
if (tag === "[object Set]") {
// @ts-ignore
value.forEach((subValue) => {
result.add(deepCopyObject(subValue, hash));
});
}
for (const key in value) {
if (Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(value, key)) {
// 열거 가능한 자체 속성을 재귀적으로 복제 및 할당합니다.
result[key] = deepCopyObject(value[key], hash);
} else {
result[key] = value[key];
}
}
return result;
};
const 순환참조가_있는_객체를_완전히_복사하는지_검사 = (): boolean => {
const object = {
foo: { b: { c: { d: {} } } },
bar: {},
};
object.foo.b.c.d = object;
object.bar.b = object.foo.b;
const copied = deepCopyObject(object);
return copied.bar.b === copied.foo.b && copied !== object && copied === copied.foo.b.c.d;
};
console.log(순환참조가_있는_객체를_완전히_복사하는지_검사());
// => true순환 참조가 있는 객체를 완전히 복사하는지 검사한 결과도 true로 잘 나옵니다.
이쯤되면 궁금해집니다. 왜 굳이 이런 번거로움을 감수하고도 깊은 복사를 생성한다는 것이 왜 중요할 까요? 우선 깊은 복사와 얕은 복사가 뭔지 이해할 필요가 있습니다.
얕은 복사는 두 객체가 동일한 참조를 공유하기에 원본 또는 복사본이 변경되면 예상치 못한 객체가 변경되 어 디버깅이 어려워집니다. 반면, 깊은 복사는 복사된 객체의 속성이 원본 객체와 동일한 참조를 공유하지 않는 복사본을 뜻합니다.
즉, 원본이나 복사본을 변경할 때 다른 객체를 변경하지 않도록 보장받을 수 있습니다. 실수를 방지하는 것이죠.
Lodash의 cloneDeep()
import _ from "lodash";
const copiedPerson = _.cloneDeep(person);
console.log(person === copiedPerson);
// => false
console.log(person.name === copiedPerson.name);
// => false
console.log(person.address === copiedPerson.address);
// => false모든 값, 속성, 그리고 중첩된 객체까지 모두 달라 false 로 나타납니다. 그러나 외부 종속성이 추가되는 것은 피할 수 없습니다.
객체 복사 메소드별 벤치마크
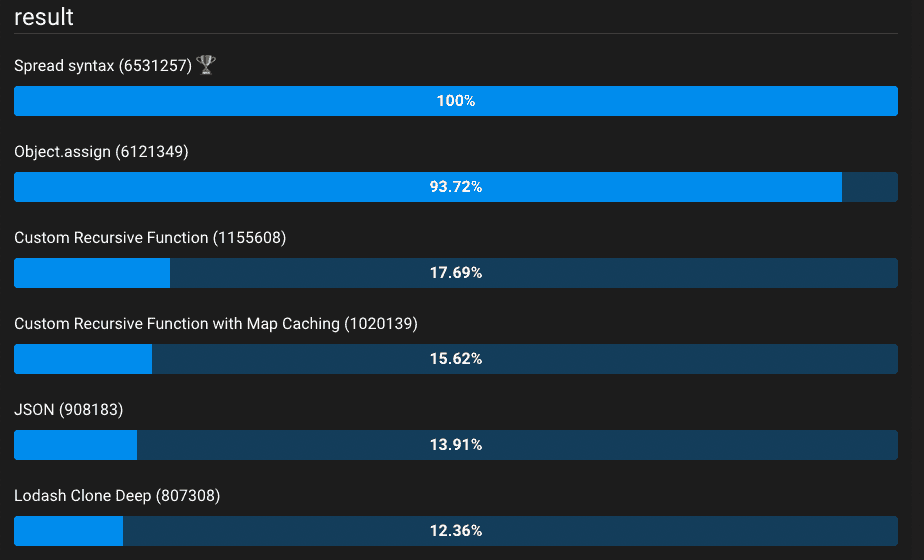
결론
- 순환 객체에 대해 지원하지 않아도 되고
Date,Map등의 유형을 보존할 필요가 없다면JSON.parse(JSON.stringify())를 사용하거나 위에서 직접 구현한Recursive Deep Clone Object처럼 구현해 사용하면 되겠습니다. - 그러나 순환 객체에 대해 지원해야 하고 여러 유형을 보존해야 한다면 lodash의
cloneDeep()이나 위에 서 구현한deepCopyObject함수를 사용하면 되겠습니다. (물론cloneDeep과 달리 구현한deepCopyObject는 모든 유형을 지원하진 않습니다.)
객체를 복사하는 데에는 많은 방법이 있습니다. 정답은 없으므로 상황에 따라 가장 적합한 방법을 선택하여 사용하면 되겠습니다.
참고
https://code.tutsplus.com/articles/the-best-way-to-deep-copy-an-object-in-javascript--cms-39655#json
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Symbol/toStringTag
https://medium.com/오늘의-프로그래밍/자바스크립트에서-object-object-가-대체-뭘까-fe55b754e709
https://github.com/lodash/lodash
https://erdem.pl/2019/08/can-json-parse-be-performance-improvement



